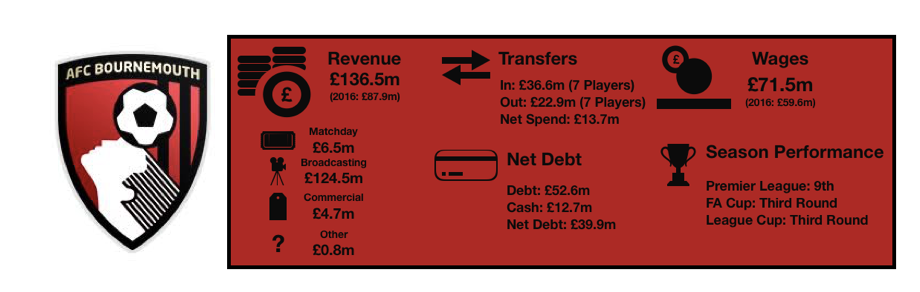
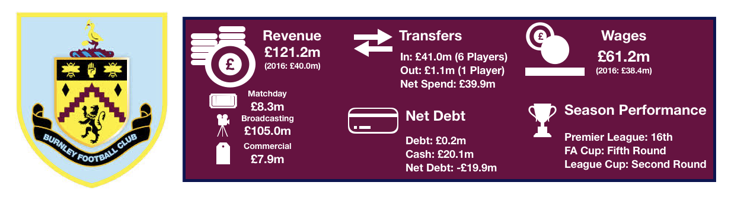
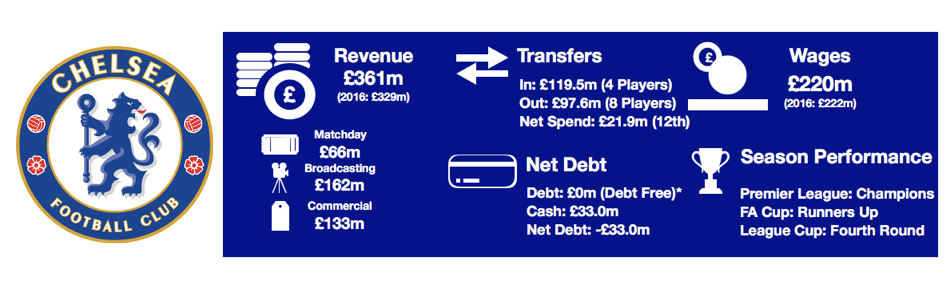
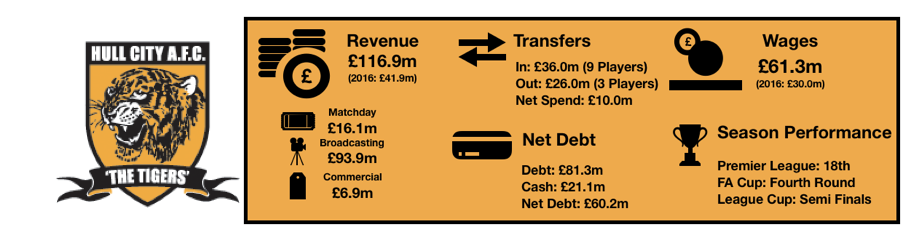
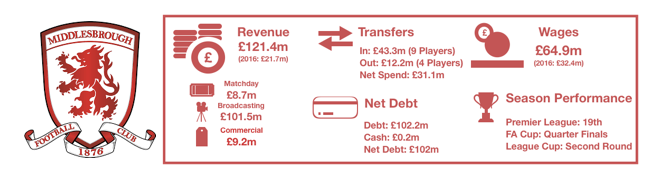
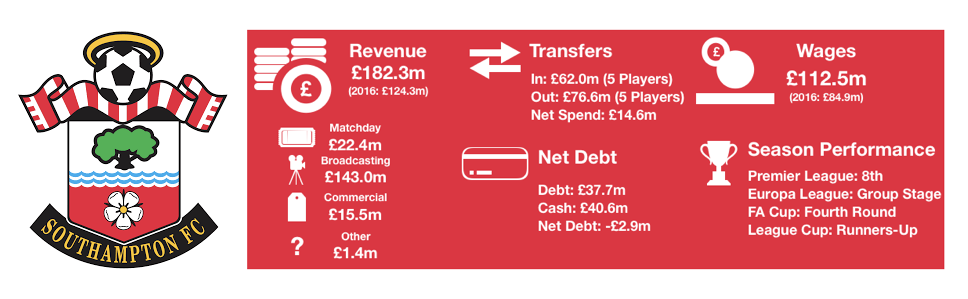
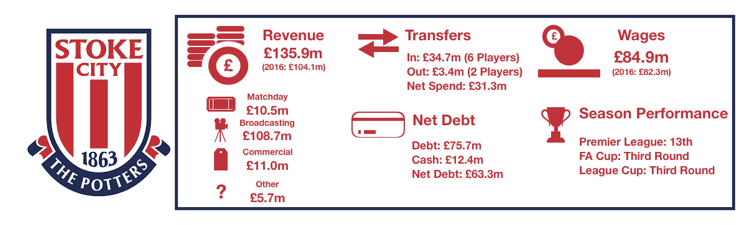
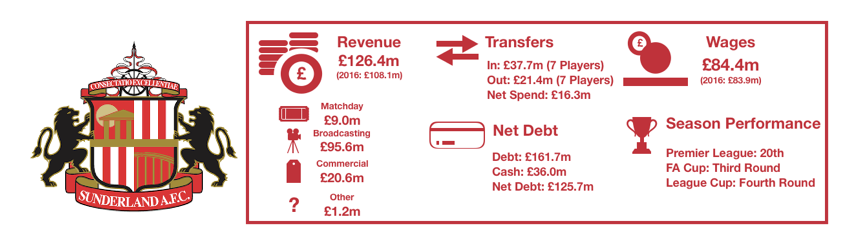
Tottenham enjoyed another fine season in what has been a great spell for the club under Pochettino, finishing 3rdand securing another season in the Champions League while at their temporary home of Wembley.
Despite this success, Tottenham were once again called out on their lack of trophies, having failed at the Semi-Final Stage, Last 16 and Fourth Round in the FA Cup, Champions League and League Cup respectively.
However, Levy has much to be happy about having steered Tottenham to this point on a low budget, helping Tottenham record a world record profit of £113.0m, up from an already impressive £36.2m (212%).
Let’s delve into the numbers.

Revenue Analysis

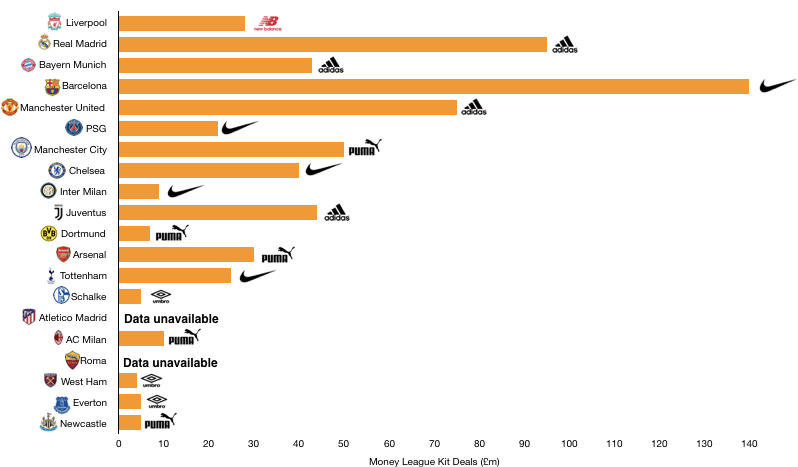
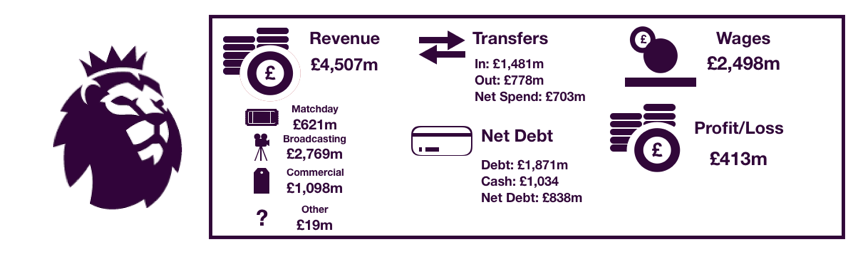
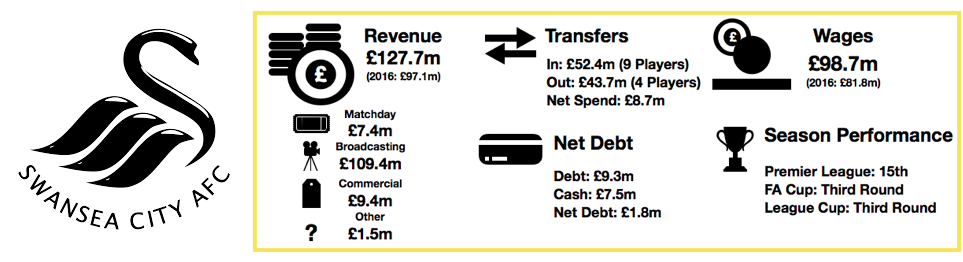
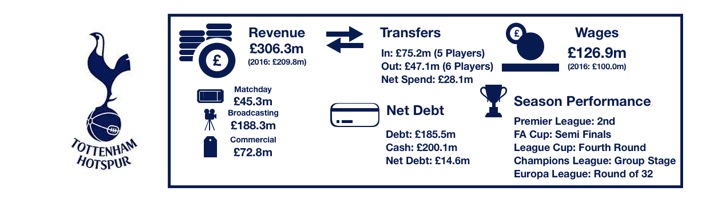
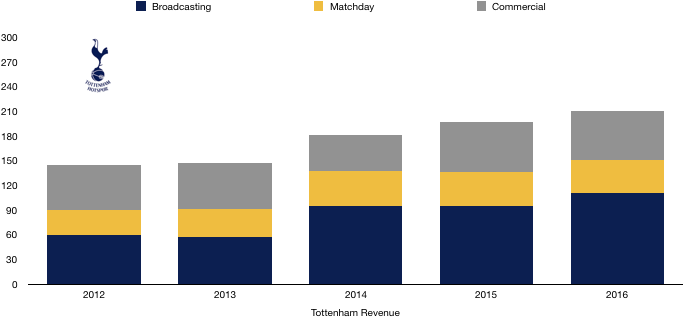
Tottenham saw their revenue increase to record levels, rising from £309.7m to £380.7m (23%) as the club benefitted from their move to Wembley and their new Nike deal.
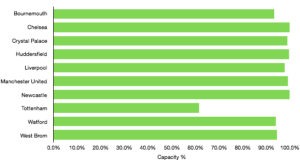
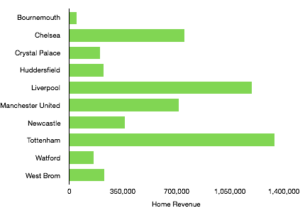
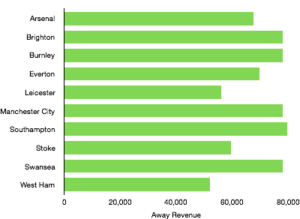
Matchday revenue increased significantly from £45.3m to £71.0m (57%) as the move to Wembley proved extremely lucrative for Tottenham. Average attendance more than doubled from 31,639 to 67,953 (115%), although to fill seats tickets were on average cheaper.
Broadcasting revenue increased from £188.2m to £200.7m (7%). This increase was mainly due to entering the knockout phases of the Champions League, having failed to in 2017, with UEFA prize money increasing from £38.4m to £53.1m (38%), while Premier League TV money actually fell from £150.0m to £147.6m (2%) as they dropped a place in the Premier League.
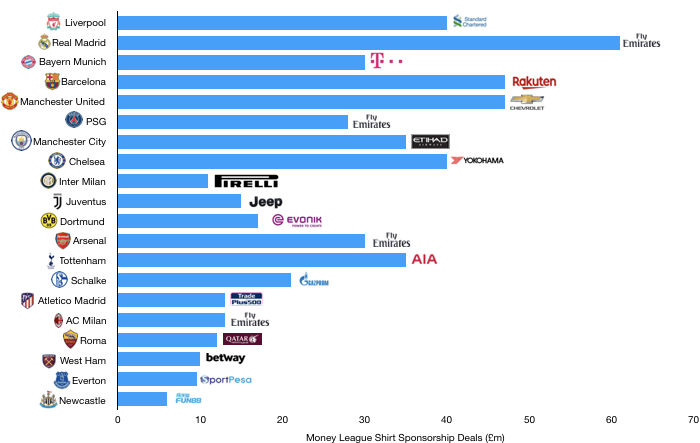
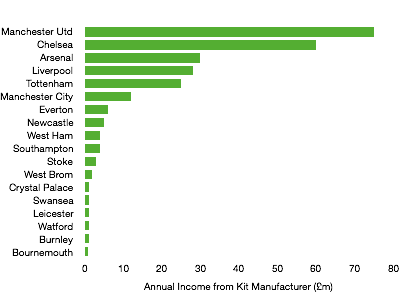
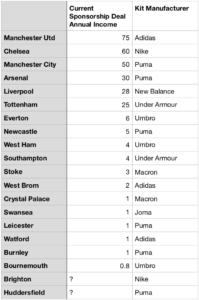
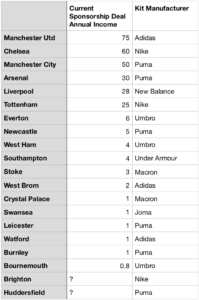
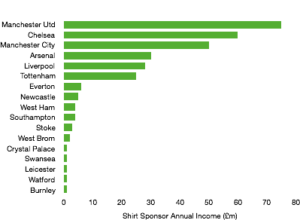
Commercial revenue grew well, rising from £76.2m to £109.1m (43%) as Tottenham replaced their deal with Under Armour (£10m per annum) with a much more lucrative 15-year deal from Nike (£30m per annum).
Looking ahead, Tottenham should see some revenue growth this year. Tottenham have played the majority of their games at Wembley again this year so matchday revenue will be relatively stable considering they will have a similar number of home games this year.
Broadcasting revenue should increase with Tottenham reaching at least the Quarter Finals of the Champions League this year. Premier League revenue is likely to fall unless Tottenham can match last seasons’ 3rdplaced finish, while they also performed worse in the FA Cup which will harm revenue in this area. Commercial revenue should also continue its upward trajectory with Tottenham’s popularity and stature continually growing.
Costs Analysis

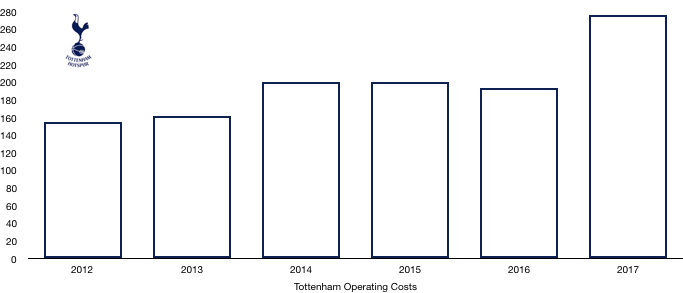
Tottenham managed their costs to perfection in 2018 under strict orders from Daniel Levy. Cost rose slightly from £276.7m to £296.7m (7%). With revenue rising by 22%, keeping costs rises down to 7% is incredible considering the higher level Tottenham have maintained, this has significantly boosted profitability.
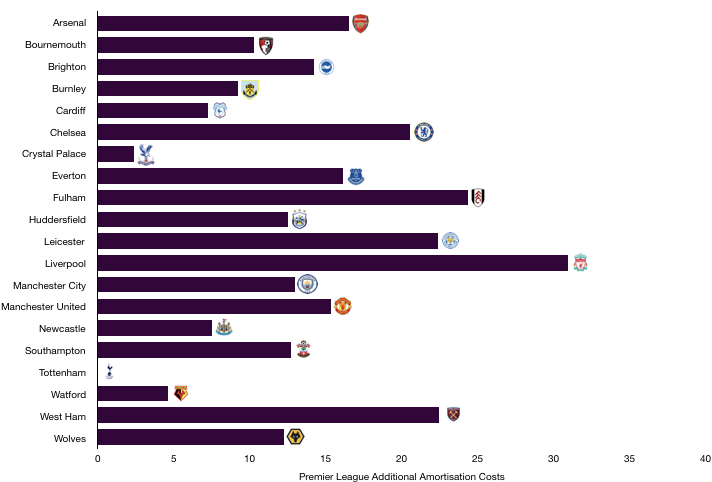
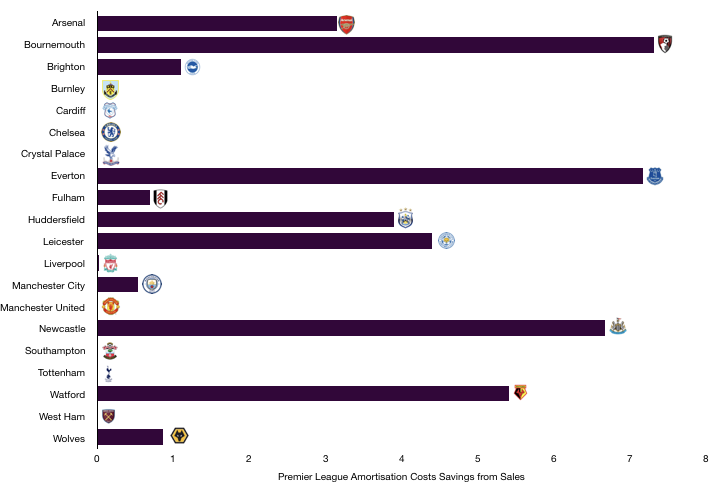
Amortisation increased from £42.9m to £57.5m (34%) after an influx of new players replaced existing players who had been at the club for some time, with the rise in amortisation signifying reinvestment.
Amortisation is likely to fall this year following little transfer activity at the North London club.
Lease costs increased from £1.1m to £1.4m (22%).
Net interest costs fell from £21.2m to £18.1m after interest rates fell on some of their loans.
Tottenham also paid tax of £26.0m, an effective tax rate of 18% which is largely in line with the statutory rate of 19%.
Tottenham stadium is the most interesting part of their current finances and the delayed entry and spiralling costs has peaked everyone’s interest.
At the beginning of the year, Tottenham had spent £517.5m after initially expecting this to be around the full cost of the stadium. However, this year they have had to fork out an eye-watering £514.1m due to overruns, taking the total costs of the stadium to over a billion pounds! This has considerably affected their finances and transfer plans, leading to additional loans (see debt analysis).

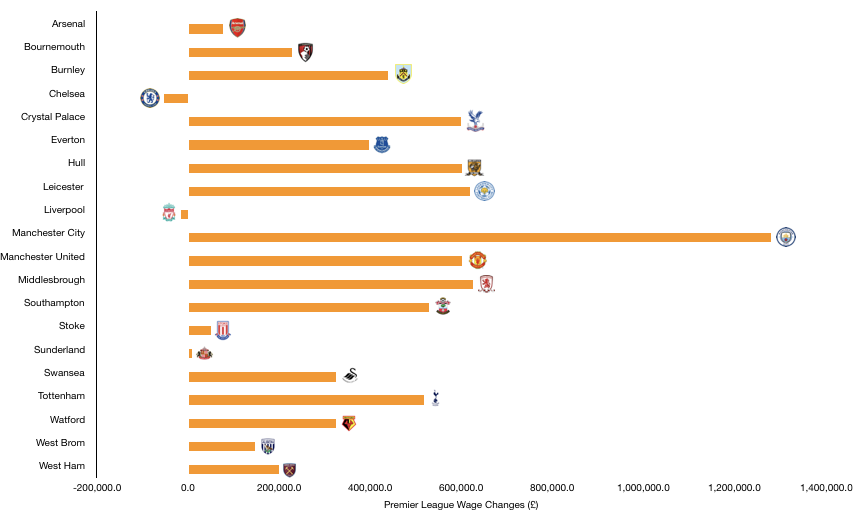
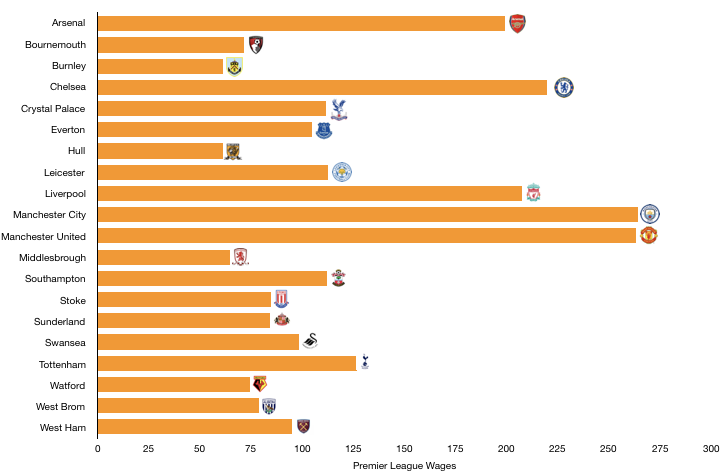
Wage control persisted this year with a stadium to pay for, but wages did still rise from £126.9m to £147.6m (18%) on the back of the new signings while their key players were rewarded with new, lucrative contracts after another excellent season.
The increase in wages works out at an extra £398k a week, the minimum Tottenham needed to remain competitive with the wage rise at their rivals surpassing this considerably.
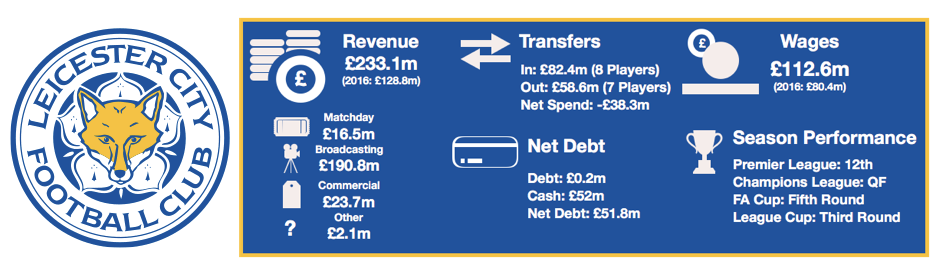
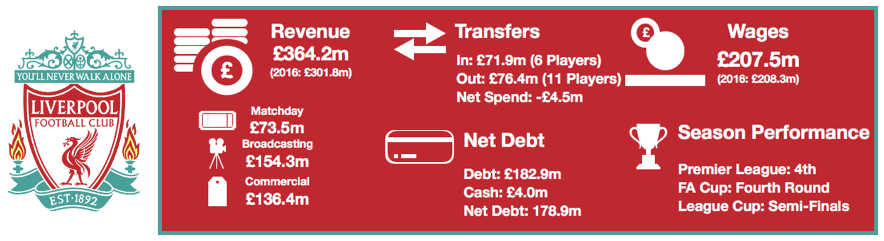
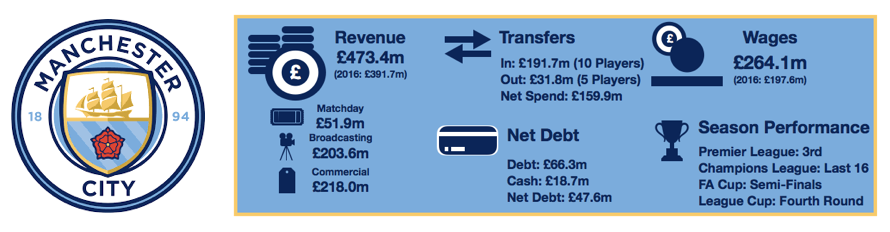
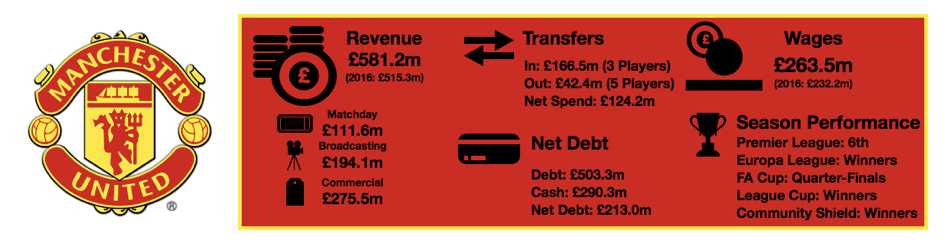
Despite this wage rise, Tottenham are still way below their rivals with United (£295.9m), Liverpool (£263.6m), City (£259.6m), Chelsea (£245.7m) and Arsenal (£240.1m) all paying well above the wages on offer at Tottenham.
This showcases what a great job the club are doing to remain competitive among these financial giants, highlighted even further by the fact Everton (£145.5m) pay around a similar amount in wages to Tottenham.
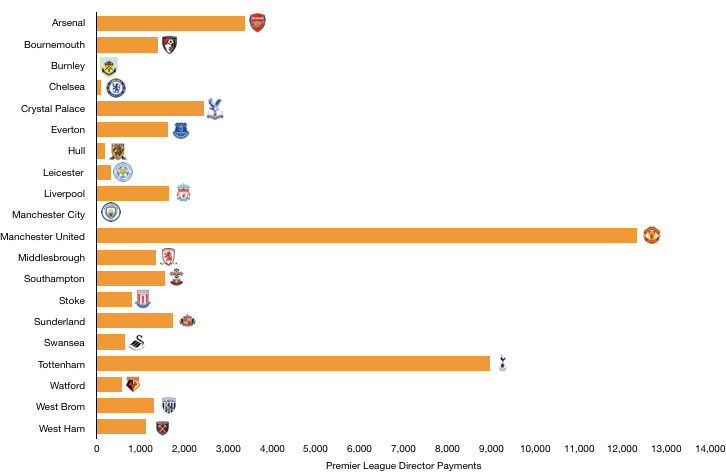
Director remuneration more than halved as they sacrificed in the short term due to the stadium, with remuneration falling from £9.0m to £4.2m (53%), while Levy saw his pay halved from £6.0m to £3.0m, with the previous bumper pay being due to back dated bonuses that hadn’t been paid, so his renumeration was always expected to decrease this year.
Looking ahead, Costs are likely to increase slightly next year. Wages will rise slightly due to new contracts with the only incoming or outgoing of note being Dembele, amortisation will fall due to the lack of investment.
Costs are likely to rise a bit due to stadium maintenance costs that will now be incurred on the New White Hart Lane following the move into the stadium this week.
Profits are likely to plummet next year despite no major increase in costs or revenue as transfer sales were a major part of their profit this year, and with no major outgoings, this will hit profit considerably as will be seen in the next section.
Transfers Analysis
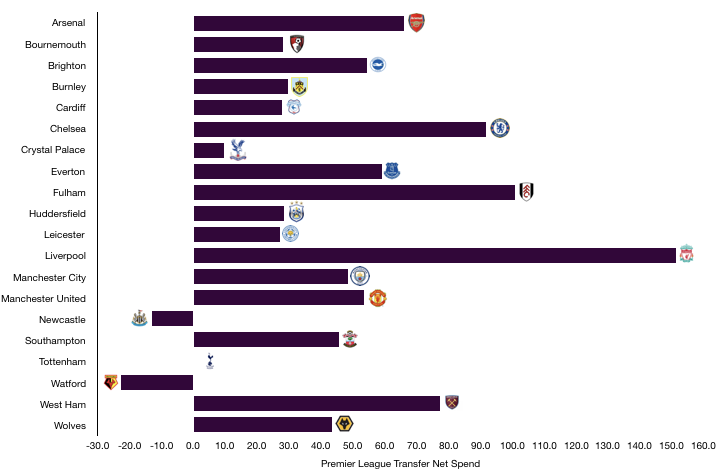
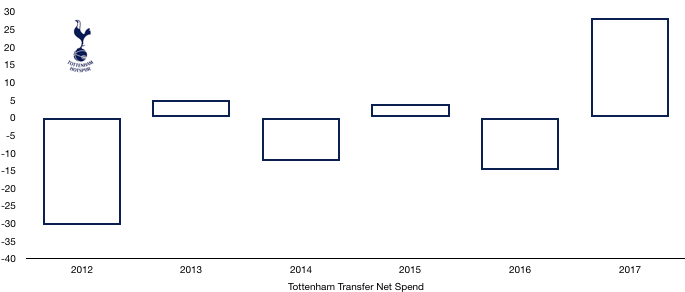
There has been little transfer activity since 2018 with Tottenham signing no players this season. However, 2018 was a busy transfer season for Tottenham as they signed 5 players and sold 6.
In came Sanchez (£36.0m), Lucas (£25.6m), Aurier (£22.5m), Lllorente (£13.6m) and Foyth (£11.7m) for a combined £109.4m.
Out went Walker (£47.4m), Wimmer (£17.5m), Bentaleb (£17.1m), N’Jie (£6.3m), Fazio (£2.9m) and Jannsen (Loan – £2.3m) for a combined £93.4m.
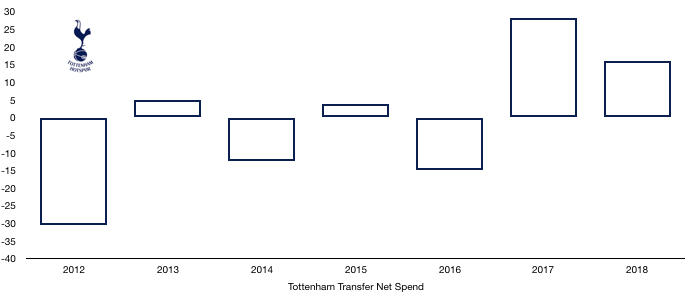
This led to a net transfer spend of £16.0m, their second successive net spend.
Sanchez, Lucas and Aurier all proved to be class signings for Tottenham, adding quality to the squad while Llorente added depth and Foyth was one for the present and future and has shown potential.
Meanwhile, Tottenham received good fees for Walker and great fees for Wimmer and Bentaleb given the quality they showed at White Hart Lane.
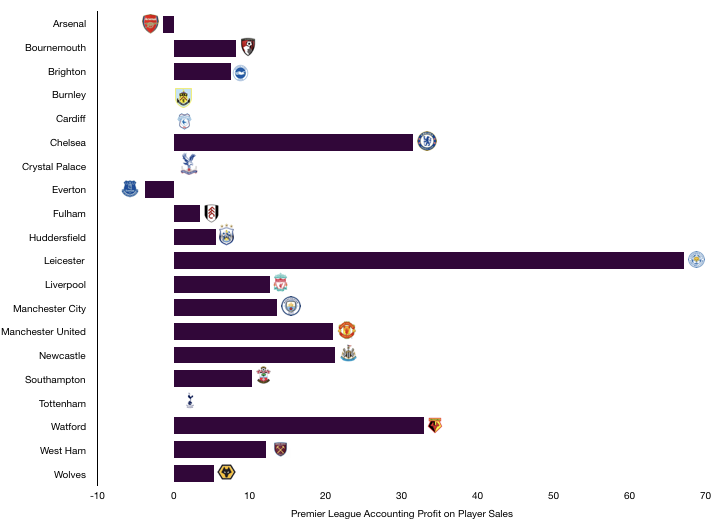
Tottenham recorded a profit on player sales of £73.1m mainly due to the sales of Walker and Bentaleb and this went a long way in securing their record profit levels. Tottenham would have still been profitable without any sales which is an impressive and unusual feat.
In cash terms, Tottenham spent cash of £79.9m and received £73.8m, a net cash outlay of a measly £6.1m which is peanuts for a club the size of Tottenham.
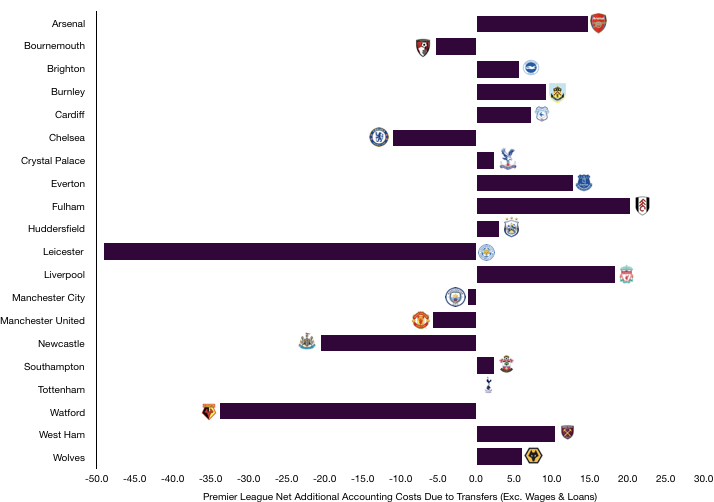
However, Tottenham do owe a further £108.4m (£44.1m of which is due this year) and are only owed £40.2m (of which £36.1m is due this year), a net owing position of £68.2m (£8.0m this year).
This has clearly (along with the bigger reason of their stadium) affected their transfer plans with this £68.2m needing to be paid in the coming season or two, hopefully they will have some cash to spend this summer.
There is also the further possibility of owing £14.9m to clubs/agents and £16.9m to players should certain transfer clauses be met, although it unlikely the full amount of either balance will ever become payable.
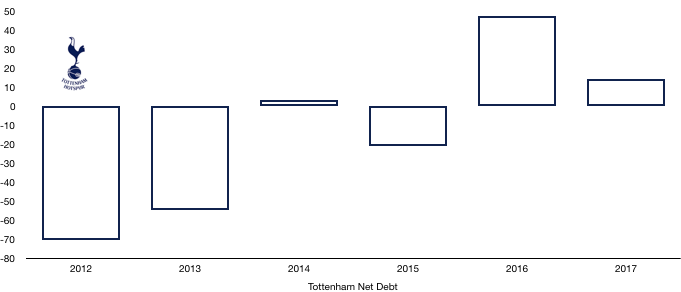
Debt Analysis

Tottenham built up a sizeable cash balance in 2017 and this was halved from £200.1m to £100.6m (50%) due to the development of New White Hart Lane.
Increased revenue and profits and the existing cash balance were used to pay for transfers and part of the huge £492.9m cash outlay Tottenham spent this year on their stadium.
This amount was nowhere near enough, so Tottenham needed new loans of £279.4m to help fund this.
Debt hence more than doubled from £185.5m to £466.3m (151%) on the back of the huge new loans needed to fund the stadium and its inevitable overruns.
Investec have loaned Tottenham £21m until 2022 as part of their stadium funding.
However, the main bulk has come from a consortium of HSBC, Goldman Sachs and America Merrill Lynch who have provided £445.3m so far, with Tottenham having the ability to increase this to £537m. All amounts are due to be repaid by 2022, which is only 3 years away and seems a push that it will all be repaid by then (it will most likely be renegotiated or refinanced elsewhere).
The average interest costs across these loans is around 3%.
Levy has pledged £50m of loans as well should it be needed, although this hasn’t been touched yet.
Tottenham hence moved from a net cash position of £14.6m to a huge net debt position of £365.7m as would be expected given the scale and ambition of their new stadium.
This represents a huge change in the debt profile of Tottenham however this stadium is going to pay dividends going forward, increasing matchday income and generating considerable commercial opportunities.
The key now is to guarantee Champions League football next season, because without it, repaying the stadium loans will become more difficult and stretch their budget further, hurting any ability to bring in new players the club desperately need to remain competitive.
It remains to be seen the full effect a demotion to the Europa League football would have, and it’s not a thought Tottenham fans or Daniel Levy even want to contemplate.
Thanks for reading – Share with a friend!